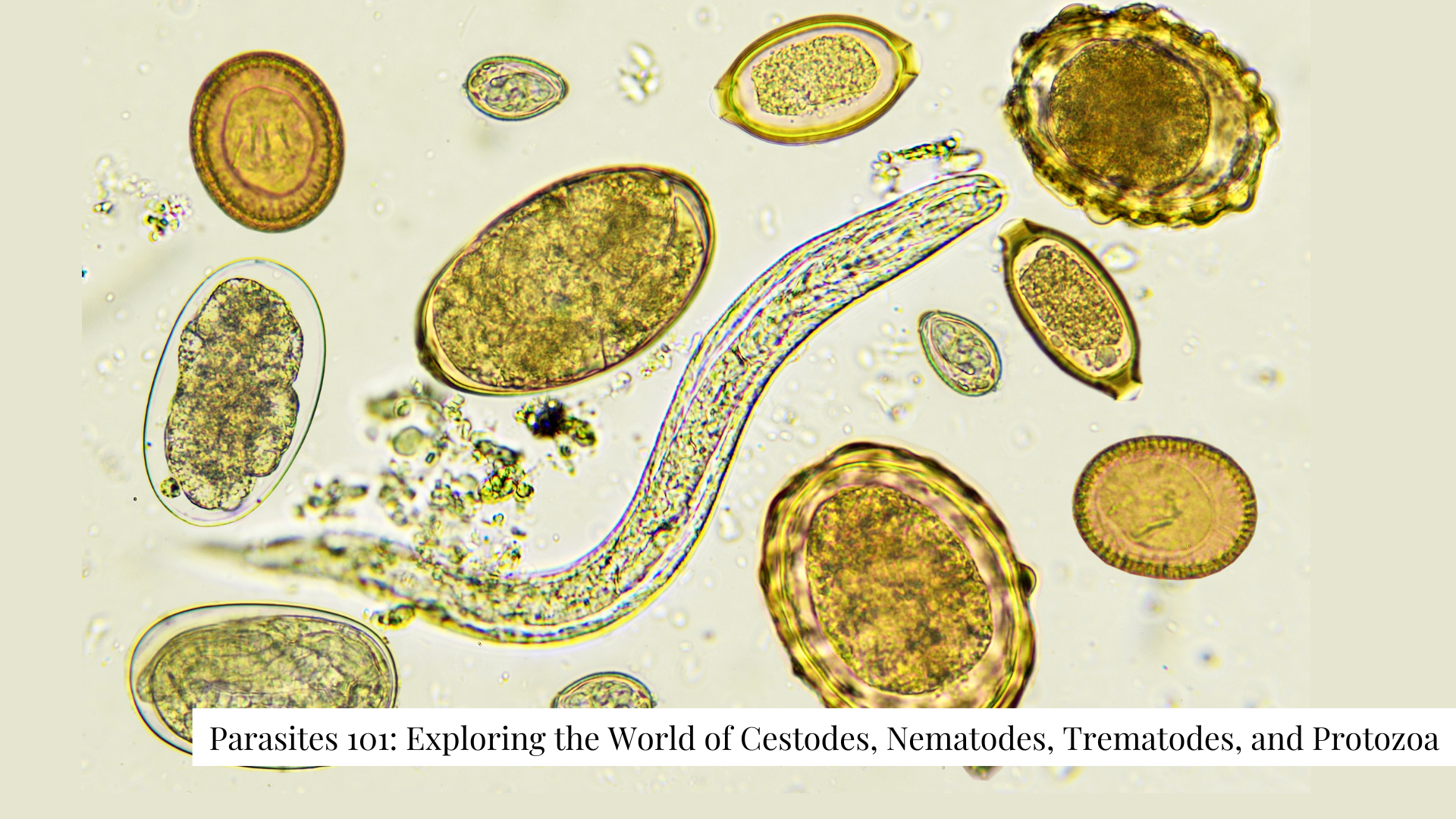
An Overview
Parasitic infections can have serious consequences for human health, particularly in individuals with weakened immune systems. In some cases, parasitic infections can lead to chronic health problems, such as Mast Cell Activation Syndrome, Lyme Disease, Leaky Gut, and even anxiety disorders and depression. Additionally, some parasites can cause long-term damage to organs and tissues, such as the liver, lungs, and brain and greatly impact quality of life
For those who suspect they could have a parasitic infection, clearing them demands attention to mitochondrial health and drainage, too, for all the ways parasites shut down important biochemical processes and normal bodily functions. The effectiveness of treatment depends on the type of parasite and the severity of the infection. In some cases, repeated treatment may be necessary to fully eliminate parasites from the body.
While parasitic infections can be a serious health concern, it’s important to remember that many individuals with parasitic infections are able to fully recover and regain their health and well-being.
Parasites 101: Exploring the World of Cestodes, Nematodes, Trematodes, and Protozoa
Cestodes, nematodes, trematodes, and protozoa are all types of parasites that can infect humans and other animals. Each of these groups of parasites has unique characteristics and can cause a range of health problems.
Cestodes
Cestodes, also known as tapeworms, are a type of parasitic flatworm that can infect the human body. These worms are long and ribbon-like and can grow up to be greater than 6.5 feet. Cestode infections are typically contracted through ingestion of contaminated food, such as undercooked meat or fish.
Cestodes can have a significant impact on human health by disrupting various physiological processes in the body. These worms reside in the digestive tract and absorb nutrients from the host’s foods and tissues, which can lead to nutrient deficiencies and other health problems. Cestode infections can also cause damage to the intestinal wall, leading to inflammation and ulceration, resulting in abdominal pain and other digestive issues.
Furthermore, cestodes can interfere with the host’s immune response, leading to an increased risk of secondary infections. These worms also release toxic substances that can cause damage to other organs, such as the liver and lungs.
In severe cases, cestode infections can cause malnutrition due to the depletion of nutrients by the parasite, neurocysticercosis, a severe infection of the central nervous system that can cause seizures, headaches, and other neurological symptoms. and intestinal obstruction: In rare cases, when cestodes grow long, they can cause intestinal obstruction, which can lead to severe pain, nausea, and vomiting. In the world of parasite cleansing, clearing cestodes comes first (with nematodes), and treatment includes anti-parasitic herbs to clear them and prevent further complications.
Cestode infections can disrupt the absorption of essential nutrients such as proteins, carbohydrates, and fats, leading to malnutrition and weight loss. These worms can also interfere with the host’s immune response, leading to an increased risk of secondary infections.
Nematodes
Nematodes, or roundworms, can cause a range of health problems due to their parasitic nature. These worms can invade various organs and tissues, leading to disruptions in several biochemical processes.
One of the primary ways nematodes disrupt biochemical processes in the body is by interfering with nutrient absorption from the gastrointestinal tract. This can lead to malnutrition, weight loss, and other related health problems. Nematode infections can also cause damage to the intestinal wall, leading to inflammation, bleeding, and other digestive issues.
Moreover, nematodes can interfere with the host’s immune system, increasing the risk of secondary infections. These worms can release toxic substances that can cause damage to organs such as the liver, lungs, and kidneys. In some cases, nematodes can also cause neurological symptoms, such as seizures and paralysis.
It is essential to treat nematode infections promptly to prevent further complications. Anti-parasitic herbs can help clear the worms and manage symptoms. Proper hygiene practices, such as washing hands thoroughly with soap and water and avoiding contact with contaminated soil and water sources, can also help reduce the risk of nematode infections.
Trematodes
Trematodes, or flukes, are a type of parasitic flatworm that can infect the human body. These worms can have a significant impact on human health and cause a range of symptoms.
Trematode infections can cause inflammation and damage to organs such as the liver, lungs, and intestines. This can result in symptoms such as abdominal pain, diarrhea, and jaundice. Trematodes can also disrupt the absorption of nutrients from the intestine, leading to malnutrition and weight loss, which can have a significant impact on a patient’s quality of life.
Moreover, trematodes can interfere with the host’s immune system, leading to an increased risk of secondary infections. Some trematodes can also release toxic substances that can cause damage to organs and tissues throughout the body, leading to chronic health problems and a decrease in the patient’s quality of life.
In severe cases, trematode infections can cause significant morbidity and mortality. Some types of trematodes cause liver damage, which can progress to liver cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma, a type of liver cancer.
Prompt treatment of trematode infections is essential to prevent further complications and improve the patient’s quality of life. Anti-parasitic herbs help eradicate the worms and manage symptoms.
Protozoa
Protozoa are a diverse group of unicellular organisms that can have varying impacts on human health, depending on the type of protozoan and the patient’s immune status. Some protozoa can cause severe health problems that affect the patient’s quality of life.
Protozoan infections can lead to a range of symptoms, including diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, and fever. In some cases, these infections can cause significant chronic illness, particularly in patients with weakened immune systems, such as those with HIV/AIDS or cancer.
For example, some protozoa such as Plasmodium spp., which cause malaria, can lead to severe anemia, which can have a lasting impact on a patient’s health and quality of life. Similarly, Toxoplasma gondii, a protozoan that can cause toxoplasmosis, can have severe effects on the developing fetus during pregnancy, leading to neurological problems and other health issues.
Protozoan infections can also cause chronic health problems, such as Chagas disease, caused by Trypanosoma cruzi, which can lead to heart failure and other complications that affect a patient’s quality of life.
Prompt diagnosis and treatment of protozoan infections are essential to prevent further complications and improve the patient’s quality of life. Treatment typically involves anti-parasitic medication to eradicate the protozoa and manage symptoms. Patients should also be advised on proper hygiene practices, such as washing hands thoroughly with soap and water and avoiding contact with contaminated food and water sources, to reduce the risk of infection.
In Conclusion
Parasites are a diverse group of organisms that can have significant impacts on human health. Cestodes, nematodes, trematodes, and protozoa are common types of parasites that can cause a range of symptoms and health problems. These parasites can disrupt various biochemical processes in the body, leading to malnutrition, weight loss, organ damage, and other chronic health challenges and complications.
Diagnosis and treatment of parasitic infections are essential to prevent further problems and improve quality of life. Treatment typically involves anti-parasitic herbs to clear the parasitic infections.
Understanding the world of parasites is essential for all of us today. Awareness of the risk factors and potential problems caused by parasitic infections is no longer optional in the toxic world we live in. By taking preventive measures and seeking timely treatment, you can reduce the impact of parasitic infections on your overall health and quality of life!
To discuss your health goals and explore my coaching options, email me here.
Resources For Your Review
There are numerous articles that discuss the relationship between cestode infections and chronic illness published on PubMed. PubMed is a free, online database maintained by the National Library of Medicine (NLM) that provides access to a vast collection of biomedical literature, including journal articles, book chapters, and conference proceedings. PubMed contains more than 30 million citations and abstracts from over 5,500 journals in the fields of medicine, nursing, dentistry, veterinary medicine, and related areas. Some of the most relevant articles I referenced for this post include:
“Chronic infection with Taenia solium and Taenia saginata: From clinic to biology” by D. D. Díaz et al. (2018): This review article discusses the clinical manifestations and pathogenesis of chronic infection with Taenia solium and Taenia saginata, two common cestode species. The authors highlight the importance of early diagnosis and treatment to prevent the development of chronic illness. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6060351/
“Neurocysticercosis: a review on status in India, management challenges, and new drug options” by R. J. Mahajan et al. (2017): This article provides an overview of neurocysticercosis, a parasitic infection of the central nervous system caused by Taenia solium. The authors discuss the challenges of managing chronic neurocysticercosis and highlight new drug options that may offer improved treatment outcomes. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5482324/
“Cysticercosis and Neurocysticercosis as Causes of Seizures in the United States” by H. H. Garcia et al. (2018): This study examines the prevalence and clinical characteristics of cysticercosis and neurocysticercosis in the United States. The authors note that chronic neurocysticercosis can lead to seizures and other neurological symptoms that require ongoing medical management. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5940145/
“Echinococcosis: a review of the epidemiology and transmission of a common parasitic disease” by P. Kern et al. (2016): This review article provides an overview of echinococcosis, a parasitic infection caused by the tapeworm Echinococcus granulosus. The authors discuss the chronic nature of the disease and the challenges of managing patients with advanced stages of infection. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4721110/
“Chronic strongyloidiasis – don’t look and you won’t find” by R. S. Miller et al. (2015): This article discusses the clinical presentation, diagnosis, and treatment of chronic strongyloidiasis, an infection caused by the nematode Strongyloides stercoralis. The authors emphasize the importance of increased awareness and screening for this infection in high-risk populations, particularly those with chronic illnesses or who have received immunosuppressive therapy. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4320044/
“Chronic Fascioliasis in Humans: A Review” by G. Mas-Coma et al. (2013): This article provides an overview of chronic fascioliasis, a trematode infection caused by the liver fluke Fasciola hepatica. The authors discuss the clinical manifestations, diagnosis, and treatment of the infection, as well as the challenges of managing chronic cases. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3794977/
“Cryptosporidiosis: An Update” by L. Checkley et al. (2015): This article provides an update on cryptosporidiosis, a protozoan infection caused by the parasite Cryptosporidium. The authors discuss the epidemiology, clinical manifestations, diagnosis, and treatment of the infection, and highlight the challenges of managing chronic cases in immunocompromised patients. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4460795/
“Chronic amebiasis: a new perspective on an old disease” by J. A. Stanley Jr et al. (2015): This article provides a new perspective on chronic amebiasis, a protozoan infection caused by the parasite Entamoeba histolytica. The authors discuss the clinical manifestations, diagnosis, and treatment of the infection, and highlight the challenges of managing chronic cases, particularly in asymptomatic carriers. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4360400/
“Chronic intestinal schistosomiasis: challenges and opportunities for innovative control” by A. J. Fenwick et al. (2012): This article discusses the challenges and opportunities for innovative control of chronic intestinal schistosomiasis, a trematode infection caused by Schistosoma mansoni. The authors emphasize the importance of early detection, prevention, and treatment of the infection to prevent the development of chronic disease and improve patient outcomes. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3414535/
These articles highlight the importance of understanding the relationship between parasitic infections and chronic illness, as well as the challenges of managing chronic cases. Early diagnosis and appropriate treatment are critical for preventing the development of chronic disease and improving your health.
I hope you find this post and these resources helpful!





